Melanoma, an aggressive form of skin cancer, is seeing an alarming increase in cases among people under the age of 50. This alarming figure has caught the attention of the scientific community and requires greater awareness of preventive measures and the need to recognize symptoms in time for early diagnosis. In this article, we’ll explore the risk factors, signs, and symptoms of skin cancer, as well as provide insight into prevention and treatment strategies.
Skin cancer in the fifties
Melanoma is a form of skin cancer that arises from cells that produce skin pigment, known as melanin. These cells, called melanocytes, are responsible for giving color to the skin and are mainly concentrated in the upper layers of the epidermis. Skin cancer can be caused by damage to melanocyte cells from overexposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or other sources of ultraviolet light, such as tanning beds.
skin cancer
the skin cancer It has become one of the most worrisome forms of skin cancer, with a significant impact on public health. In recent decades, there has been a file He increases In the number of melanoma cases among young people, especially those under the age of fifty. This trend is concerning, as melanoma has the potential to spread to other organs in the body, making treatment more complicated.
Risk factors for skin cancer in the 50s
There are many risk factors Known to develop skin cancer:
- UV exposureExcessive exposure to sunlight or tanning lamps is a major risk factor for the development of skin cancer. It is important to protect your skin from UV rays by wearing protective clothing and using regular, broad-spectrum sunscreens.
- Clear skinLight-skinned people have a higher sensitivity to the damage caused by UV rays and are therefore more likely to develop skin cancer.
- family historyPeople who have first-degree relatives (parents or siblings) with skin cancer are at increased risk of developing the disease.
- Atypical molesHaving a large number of atypical moles, that is, moles that are irregular in shape and color, increases the risk of skin cancer.
Signs and symptoms of skin cancer
Skin cancer can develop anywhere on the body, although it is most common on sun-exposed areas such as the face, neck, arms, and legs. the Signs and symptoms of skin cancer can include:
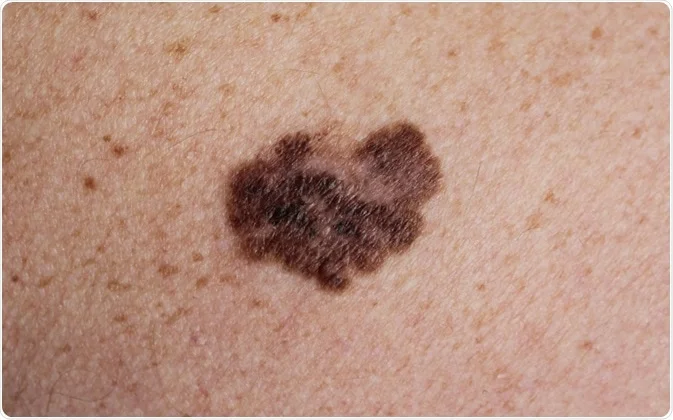
- Changes in existing molesA mole that changes shape, size, or color or itches can be a sign of skin cancer.
- asymmetryBorders of a melanocytic mole tend to be irregular and asymmetrical.
- irregular bordersThe edges of the mole may appear jagged or blurry.
- different colorsThe nevus of melanoma can be different colors, such as brown, black, blue or red.
- DiameterA melanoma nevus is often larger than 6 mm.
- developmentChanges in a mole over time, such as growth or bleeding, are symptoms of cause for concern.
If you notice any of these signs or symptoms, it is essential that you see a dermatologist immediately for a thorough evaluation.
Prevention and treatment of skin cancer
Prevention is essential to reduce the risk of skin cancer. some Useful Tips Includes:
- Sun protectionWear protective clothing and use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF.
- Avoid direct exposure to the sun: Try to avoid sun exposure during the hottest hours of the day (usually between 10am and 4pm).
- Check the skin regularlyCheck the skin regularly for changes in existing moles or the appearance of new moles.
- Consult a dermatologistMake regular visits to a dermatologist for a professional skin evaluation.
If skin cancer is caught early, treatment can be more effective and the chances of a cure better. Treatment options include surgery to remove the tumor Targeted therapy and the ImmunotherapyWhich stimulates the immune system to fight cancer.
conclusions
Melanoma is a serious public health problem, especially among those under the age of 50, so awareness of risk factors, signs and symptoms, as well as preventive measures is essential to combating this disease. Prevention and early diagnosis are essential to improve survival and reduce the impact of skin cancer on health.
sources

“Food expert. Unapologetic bacon maven. Beer enthusiast. Pop cultureaholic. General travel scholar. Total internet buff.”




